Investing into the air traffic control system and its modernization is an integral part of the constant process of ensuring and improving the quality of CNS services provided in air navigation. CNS infrastructure within SMATSA llc, which serves as a backbone for provision of air traffic services, is commissioned and operated in accordance with the international standards and requirements such as relevant ICAO Annexes and documents, the requirements set out by European Commission implementing regulations and recommendations defined by EUROCONTROL, as well as with applicable national laws and regulations. Investments in the improvements of CNS systems and equipment contribute to ensuring compliance with applicable regulations, as well as adequate air traffic capacity and safety levels.
Existing CNS infrastructure within SMATSA llc consists of accurate and reliable technical systems featuring high availability as well as high level of automation and remote supervision and control, while fulfilling contemporary environmental protection standards. High availability and continuity of CNS infrastructure and services provided thereof are achieved and guaranteed by technical systems’ design, equipment redundancy, and also significantly contributed by usage of prescribed detailed operational instructions, preventive maintenance procedures, up-to-date technical manuals, 24-hour technical supervision and management of the systems by competent, fully-trained personnel.
SMATSA’s CNS department responsibility is development, modernization and maintenance of:
- Automated Air Traffic Control Systems,
- Telecommunications Systems,
- Surveillance Systems,
- Ground Based Radio Navigation Systems,
- Automated Weather Observation Systems (AWOS) and Equipment,
- Electric Power Systems,
- HVAC systems,
- Simulation, test and training systems.
CNS department within SMATSA is certified for ATSEP training in the domain of CNS systems and equipment
Automated Air Traffic Control Systems
Automated air traffic control systems include:
- ATM systems (Surveillance and Flight Data Processing Systems),
- AFTN/AMHS system.
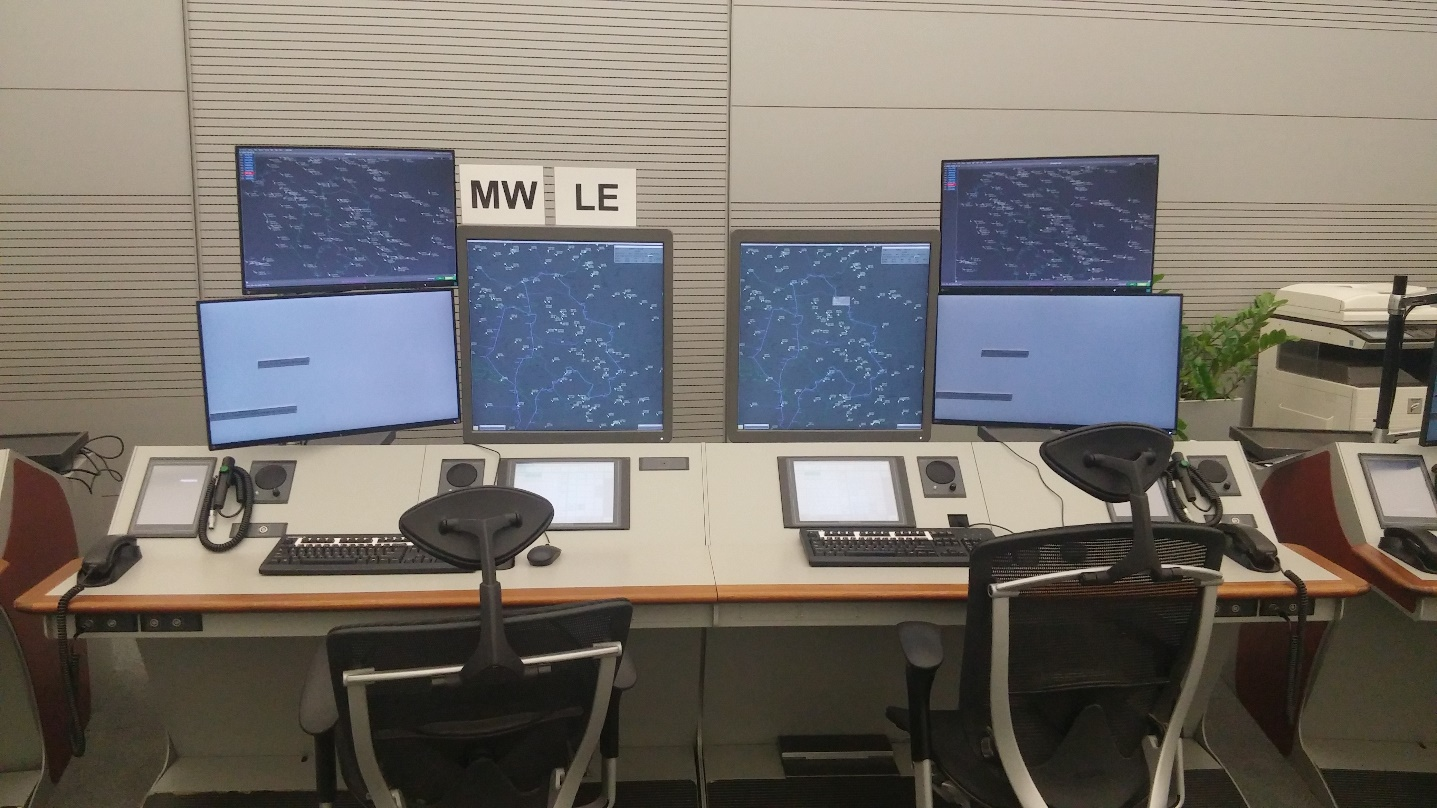
ATM systems
ATM systems represent surveillance and flight data processing systems (SDPS/FDPS) and are divided in two major parts:
- Main ATM system (TopSky-ATC system)
- Fallback ATM system (FASOS)
Main ATM system (TopSky-ATC) is a system designed to provide Air Navigation Service Providers (Air Traffic Control Centre and Towers) with operational ATC capabilities as well as training and system test capabilities.
In order to meet the high level of availability required for Air Traffic Control system, TopSky-ATC is based on a modular and distributed architecture. Multiple LANs, multiple and duplicated data processing allow to reduce the impact of failures on the ATC capabilities. The principle of distributed processing developed for TopSky-ATC ensures the safe, uninterrupted provision of Air Traffic Services in accordance with the standards recommended by international practice.
Main ATM system (TopSky-ATC system) includes operational ATM system located in ATCC Beograd including remote suites in Beograd TWR, Podgorica TMA/TWR, Batajnica TWR, Niš TWR, Kraljevo TWR and Tivat TWR.
Part of Main ATM system are Test ATM systems (BET1 and BET2) located in ATCC Beograd, which are primarily used for testing of new system configurations, software releases and parameters prior to allowing their operational use, but also for training of technical personnel and Training ATM system (BETR) located in ATCC Beograd, which is used for ATCOs training.
Main ATM system (FDPS/SDPS) is a complex multiple-purpose system, which comprises the following functions: Airspace and Centre Configuration function, Surveillance Data function, Safety Nets function, Flight Data function, Monitoring Aids function, Operational Display System function, External Communications Management function, Air-Ground Data Link function, InterOperability and Data Exchange Function, Flight Plan Conflict Probe function, Aeronautical Information System function, Communication Data Processing function, System Control and Monitoring function, System Parameter Management function, Data Recording function, Data Playback function and Data Analysis function.
SDPS provides the air traffic control officer with the information on the true aircraft position, whereas FDPS processes all flight-related data (e.g. aerodrome of departure and calculated take-off time, aerodrome of destination and landing time, requested flight level, aircraft type and appropriate equipment, etc.). SDPS and FDPS are interconnected, which enables coupling of the true aircraft position data and the flight plan data, further enabling Air Situation Display function, potential conflict identification function and alert function, and consequently facilitating work of an air traffic control officer.
Local FDPS in Belgrade is connected to global systems through which it receives initial flight plans, but is also connected to other surrounding local FDPS with which it exchanges data related to flights transferring from one air traffic control unit area of jurisdiction to another. Coordination between adjacent air traffic control units is supported with the exchange of OLDI (On-Line Data Interchange) messages (currently available OLDI connection with neighboring partners Budapest, Zagreb, Sofia, Skopje, Tirana, Brindisi, Bucharest, KFOR sector and Sarajevo).
Surveillance Front-End processors are used as integral part of Main ATM system, providing initial processing and distribution of sensor data to different internal and external users. At the moment two systems are being operated, SDDS-NG (Surveillance Data Distribution System – New Generation), as a main front-end processor and ADR (Automatic Data Replicator) system as a fallback. Front-End processors are also used for sensor data sharing with neighboring ATC units.
Fallback ATM system (FASOS) provides an operational backup system to the main SMATSA ATM system for providing a set of ATM functions. It is one application software system installed on two operational (ONL) and one test (TEST) hardware configurations.
The FASOS ONL subsystem in Belgrade have workstations connected in Beograd ACC/TMA and Beograd TWR.
The FASOS ONL subsystem in Podgorica have workstations connected in Podgorica TMA/TWR.
The TEST system mimics the ONL system and it is installed in Belgrade. It executes exactly the same software and adaptation but within a different configuration.
When the main SMATSA ATM system is in service, FASOS is able to maintain operational readiness and data integrity to enable immediate changeover of service. Data are synchronized with the main system through the dedicated interface. When FASOS is in service it is able to operate autonomously to support a set of ATM functions for providing ATS at defined capacity.


AFTN/AMHS
AFTN/AMHS is used for generation and exchange of messages in the Aeronautical Fixed Telecommunication Network (AFTN), as well as within the Aeronautical Message Handling System (AMHS).
AFTN/AMHS is physically divided into two functional units:
- Operational AFTN/AMHS unit,
- Test AFTN/AMHS unit, which is primarily used for training of operational and technical personnel, but is also used for testing of new system configurations.
The operational and the test systems are functionally identical, the only difference being that the operational system is redundant, whereas the test system has no redundancy in regard to hardware and software configuration. The operational and the test system interconnection enables availability of real messages in the test environment, which enhances not only the quality of the personnel training but also the reliability of the test results.
Depending on the primary function, AFTN/AMHS is divided in:
- AIDA-NG system, used for the exchange of AFTN/AMHS messages with the international partners (currently available AMHS connection with Athens, Banja Luka, Bucharest and Sofia and AFTN connection with Vienna, Skopje and Budapest) and external systems (main and fallback ATM systems, MET systems, etc.), and
- CADAS system, used for the exchange of AFTN/AMHS messages with domestic users in Beograd ATCC, Beograd Tower, Podgorica TMA, as well as in Batajnica, Vršac, Niš, Kraljevo, Užice and Tivat aerodrome control units (including military units and other non-SMATSA users).
Telecommunications Systems
The role of the telecommunications systems within the air traffic control system is the provision of the following services:
- Air-ground pilot-controller voice communication, for the purpose of coordination of aircraft in flight;
- Ground-ground voice communication between adjacent air traffic control units, for the purpose of coordination of aircraft in flight;
- Voice communication recording;
- Reference time distribution;
- Connection of relevant sites via transport network to provide voice communication services, exchange of OLDI and AFTN/AMHS messages, METEO and radar data, remote monitoring and control data for different systems as well as administrative IT network WAN connections, etc.
Voice communication systems provide means of air-ground and ground-ground communication at Air Traffic Control Operator positions in ATCC Beograd and all TMAs/TWRs in responsibility of SMATSA.
Voice communication system is highly reliable and fully duplicated system providing high availability of voice communication. In case of the main system failure, ATCC Beograd and TWR Beograd are using completely independent backup system, whereas TMA/TWR Podgorica is using independent radio backup system.
Radio system used for the needs of air-ground voice communication comprises a group of distributed radio centers, in order to achieve the best possible radio signal coverage. All radio center signals are collected in the Air Traffic Control Center through telecommunications network owned and managed by SMATSA llc, as well as through the telecommunications service provider’s infrastructure. Redundant paths are used wherever operationally and technically justified.

Each aeroport has its own local radio center used for air-ground communication in its area of responsibility. All frequencies used for air-ground voice communication are coordinated at the international level under the ICAO and EUROCONTROL supervision.


Some of remote radio centers
Due to the legal obligation of recording and filing of all the data relating to the process of air traffic control service provision, a system for operational voice communication recording is implemented.
Surveillance Systems
Surveillance of the air traffic under the responsibility of SMATSA llc currently relies on the use of Primary Surveillance Radar (PSR) and Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) systems.
SMATSA llc operates four radar stations (three are co-located primary and secondary radars, one is a stand-alone secondary radar). For the purpose of air traffic surveillance, radar data generated from SMATSA radars is used along with the radar data obtained through the exchange with the neighboring ANSPs. Such surveillance system architecture provides data required for multi-radar tracking and ensures fulfillment of the following requirements in accordance with the European air traffic surveillance standard:
- double secondary radar coverage in en-route,
- double secondary radar coverage and single primary radar coverage in the main terminal control areas.
All SMATSA secondary surveillance radars feature MSSR and Mode S operation modes, whereas primary surveillance radars have the ability of generating weather data. Since 2015, SMATSA llc has implemented Enhanced Mode S on all of its existing secondary radars, thus complying with the requirements set out by relevant European Commission implementing regulations regarding aircraft identification and performance and interoperability of surveillance for the Single European Sky.
SMATSA’s strategy in Surveillance domain has its main focus on improving radar data quality and achieving better redundancy of surveillance coverage, and thereby enhancing overall performance of service provision, increasing safety and service continuity.
Implementation of modern surveillance systems such as multilateration and ADS-B is envisaged as a solution for the new Beograd ATC tower, with the aim of ensuring surveillance of aircraft and vehicles for modern airport ATC unit. An A-SMGCS system to be implemented at Belgrade airport should enable detection, identification and locating of both uncooperative and cooperative stationary and moving targets located on the maneuvering area, aprons and airspace around the airport, in all weather conditions, including the conditions of reduced visibility caused by fog and rain.
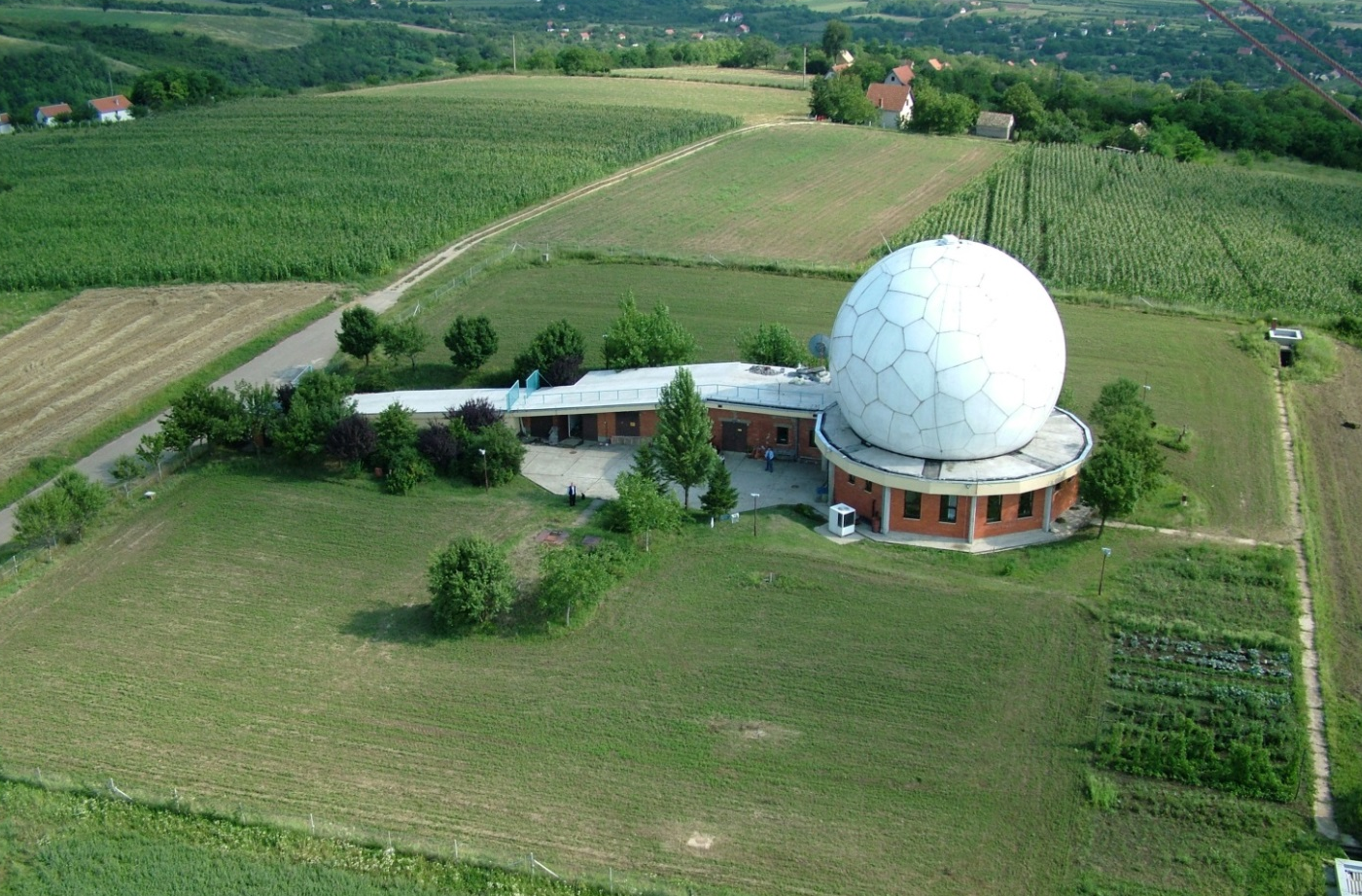



Koviona Radar Station
Ground Based Radio Navigation Systems
Ground based radio navigation aids are used in the air traffic control system in order to ensure safe en-route navigation, but also to enable the application of aerodrome instrument departure i.e. approach and landing procedures. These systems provide, at any moment, the flight crew with the possibility of determining the aircraft relative position, within the entire airspace under SMATSA llc jurisdiction, enabling the aircraft to stay on its planned course in all weather conditions. Ground based radio navigation systems are, therefore, fundamental aids in guiding the aircraft towards their destination, no matter whether they are en-route or aerodrome aids.
The main radio navigation aids within Serbia and Montenegro Air Traffic Services SMATSA llc navigation infrastructure are: ILS, VOR, DME, NDB and VDF.
Since the final approach and landing are the most complicated phases of flight, SMATSA llc is equipped with several ILS systems that enable precision instrument approach and safe landing of the aircraft, even during the low visibility conditions. ILS consists of the localizer that provides aircraft with lateral guidance, glide path that provides vertical guidance and marker beacons. The localizer guides the aircraft along the extended centreline of the runway, whereas the glide path ensures the descent of the aircraft along the glide-slope which is usually at the angle of 3º relative to the horizontal plane. Marker beacons provide indication when the aircraft is at the predefined points/distances along the approach path.
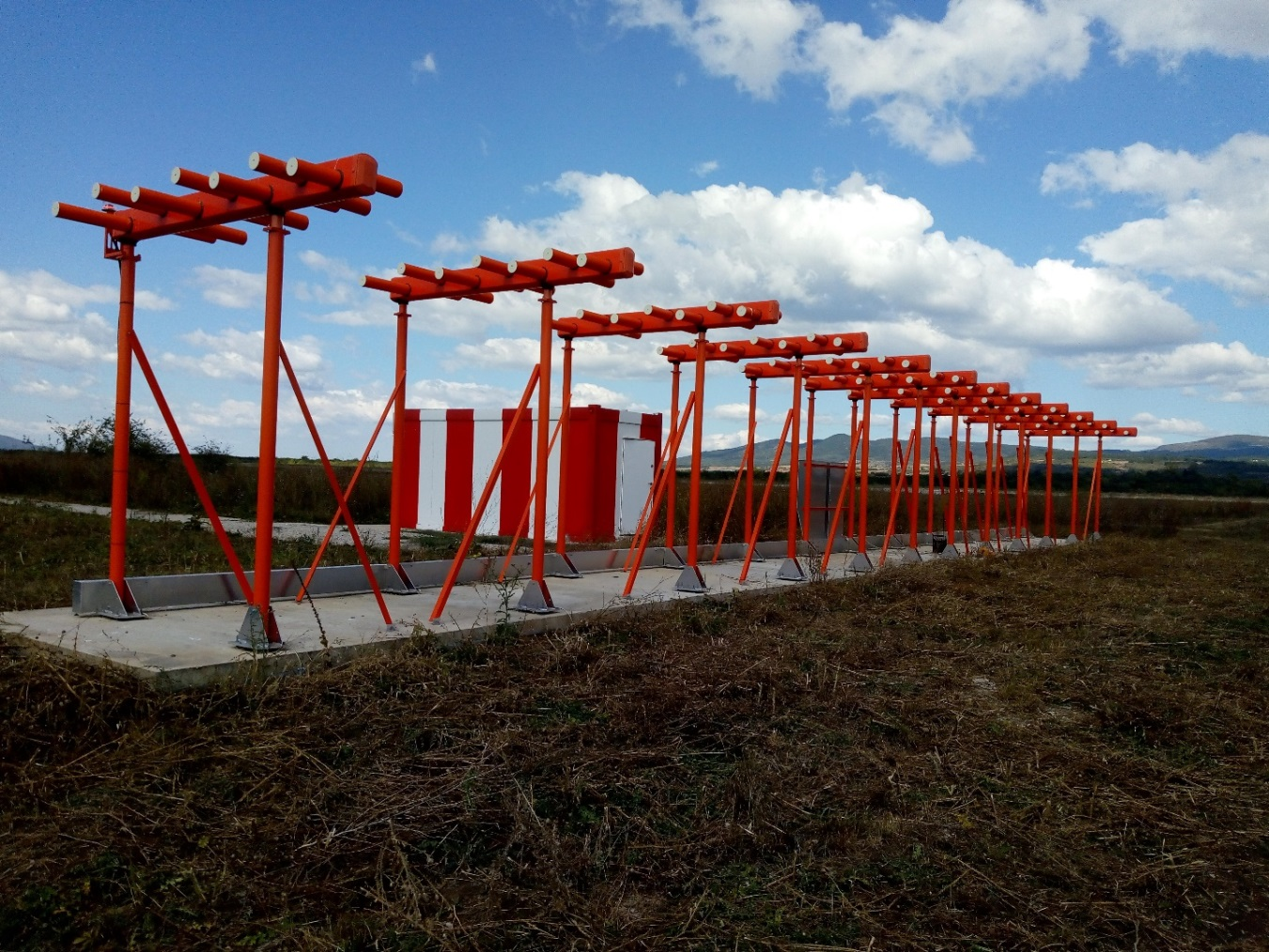



ILS Glide path with collocated DME (part of ILS/DME at Niš airport)
VOR (VHF Omni-Directional Radio Range) is a medium-range navigation aid transmitting the azimuth information. It is located along the air routes, as well as in the vicinity of the aerodromes. If the aircraft is equipped with the appropriate equipment, the pilot can determine the aircraft magnetic course in relation to the position of VOR on the ground. Two basic types of VOR exist: Conventional (CVOR) and Doppler VOR (DVOR).

DME (Distance Measuring Equipment) can be located together with VOR, so as to complement the azimuth information with the aircraft slant-range distance from VOR/DME station on the ground. The crew is provided, in this way, with all the data necessary for determining precise position of the aircraft. DME could also be coupled with ILS – instead of marker beacons, thus providing continuous information about the distance from the runway threshold.

NDB (Non-Directional Radio Beacon) is one of the earliest radio navigation aids. It is used to guide the aircraft along the air routes as well as in non-precision instrument approach for landing at the aerodrome. NDB transmits information about the aircraft relative bearing in relation to the ground station.

VDF (VHF Direction-Finder) is auxiliary navigation aid used to establish the aircraft position by determining the direction from which the radio communication, transmitted by it, is received. VDF receiver is usually located within the aerodrome complex.
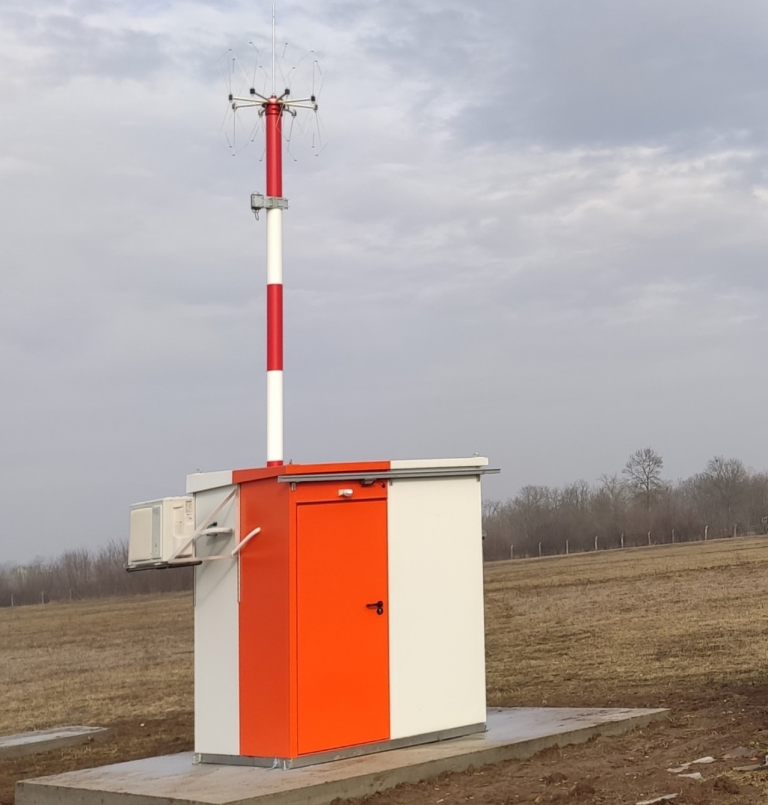

Automated Weather Observation Systems (AWOS) and Equipment
Landing at and taking off from an aerodrome depend to a large extent on current weather conditions at the aerodrome. Therefore, meteorological information is of key importance for the safety of air traffic. Automatic weather stations, which represent the main source of information, have been set up at all aerodromes in the territory of the Republic of Serbia and of the Republic of Montenegro, with the purpose of permanent measuring, collecting, processing, filing, display and exchange of meteorological data. Automatic weather stations consist of:
- sensors for measuring wind direction, wind speed, visibility, cloud height, atmospheric pressure, humidity, air and ground temperature, precipitation, etc;
- acquisition unit for reception, adjustment and forwarding the data for further processing;
- dual servers (sensor operation control, data processing, filing, transferring data to the users);
- terminal / work stations for data display.
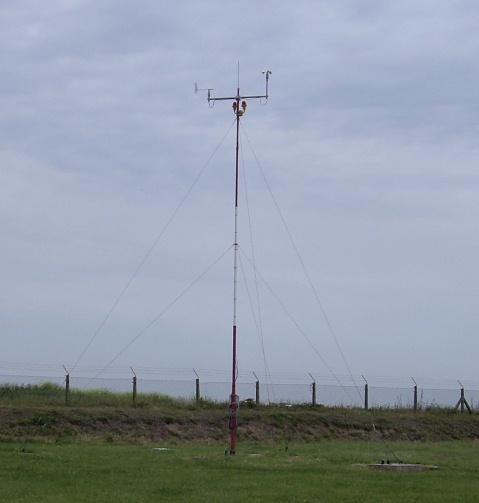

During take-off, precision approach and landing procedures in the reduced visibility conditions, apart from cloud base, the values of the Runway Visual Range (RVR) parameters are of importance. Automated system at the aerodrome in Belgrade provides these data, which was one of the conditions for establishment of operational Cat IIIb category at Nikola Tesla Airport in Belgrade.
Together with the software package for meteorological data display (SAWAS), the system includes provision of meteorological reports such as METAR, SPECI, TAF, SIGMET, AIRMET, AD WRNG, etc., which are generated either automatically or by the weather forecasters and meteorological technicians.
In order to meet the high level of availability required for meteo systems, especially in low visibility condition, automatic meteorological stations are based on a modular and distributed architecture. Multiple LANs, multiple and duplicated data processing allow to reduce the impact of failures on system capabilities. The principle of distributed processing developed in that system ensures the safe, uninterrupted provision of MET Services in accordance with the standards and international recommended practice.


Visibilimeter and present weather sensor FS11P | FS11P calibration procedure
All portable sensors are calibrated in an accredited laboratory. All measuring equipment is regularly checked and calibrated. An internal procedure prescribes the manner of calibration of meteorological equipment/instruments.

Meteorological chart from IBL prognostic system
Forecasters have at their disposal a large number of tools for visualizing phenomena and displaying meteorological maps. Several examples are given in the pictures above.
The system for detecting electrical discharge in the atmosphere should also be mentioned (picture below).
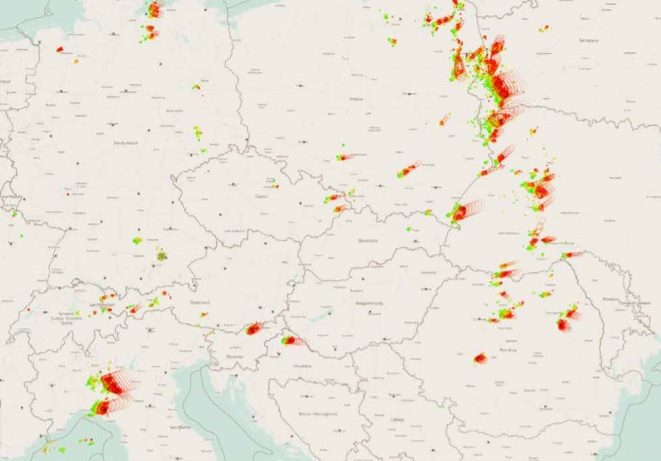
Linet system consists of field sensors, field processor and servers for calculation. The location of sensors is chosen to cover the entire territory of Serbia and Montenegro. By calculating the delay of all received information about the event, a precise place of lightning strike and lightning occurrence is obtained.
